2017. 11. 15. 13:43
matchShapes
Compares two shapes.
- C++:
matchShapes(InputArray contour1, InputArray contour2, int method, double parameter)
- Python:
cv2.matchShapes(contour1, contour2, method, parameter) → retval
- C:
cvMatchShapes(const void* object1, const void* object2, int method, double parameter=0 )
- Python:
cv.MatchShapes(object1, object2, method, parameter=0) → float Parameters: - object1 – First contour or grayscale image.
- object2 – Second contour or grayscale image.
- method – Comparison method:
CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I1,CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I2orCV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I3(see the details below). - parameter – Method-specific parameter (not supported now).
The function compares two shapes. All three implemented methods use the Hu invariants (see HuMoments() ) as follows ( 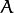 denotes
denotes object1,:math:B denotes object2 ):
method=CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I1

method=CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I2

method=CV_CONTOURS_MATCH_I3

where

and  are the Hu moments of
are the Hu moments of 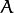 and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.
'OpenCV' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 내부 최소사각형 - minAreaRect (0) | 2017.11.15 |
|---|---|
| 내부 최대 원 찾기 - minEnclosingCircle (0) | 2017.11.15 |
| 적당한 선으로 채우기 fitLine (0) | 2017.11.15 |
| 구멍 채우기 - fitEllipse (0) | 2017.11.15 |
| 형태 볼록함 결점찾기, 구멍찾기 - convexityDefects (0) | 2017.11.15 |
